# Getting Started
## Navigation
* [Installation](#installation)
* [Build](#build)
* [User guide](#user-guide)
* [Guide to the manager](#guide-to-the-manager)
* [Guide to the editor](#guide-to-the-editor)
* [Request format](#request-format)
## Installation
Get the installation package in any of the available methods:
* [GitHub Releases](https://github.com/valentineus/moodle-webhooks/releases).
* [Compilation from the source code](#build).
### Build
Self-assembly package is as follows:
* Clone the repository:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/valentineus/moodle-webhooks.git moodle-webhooks
```
* Run the build script:
```bash
cd ./moodle-webhooks
/bin/sh build.sh
```
## User guide
After you install the plug-in, the Service Manager appears on the `Server` tab in the administration panel.
To open the page, go:
`Site administration` ->
`Server` ->
`WebHooks`.
### Guide to the manager
The main window looks like this:
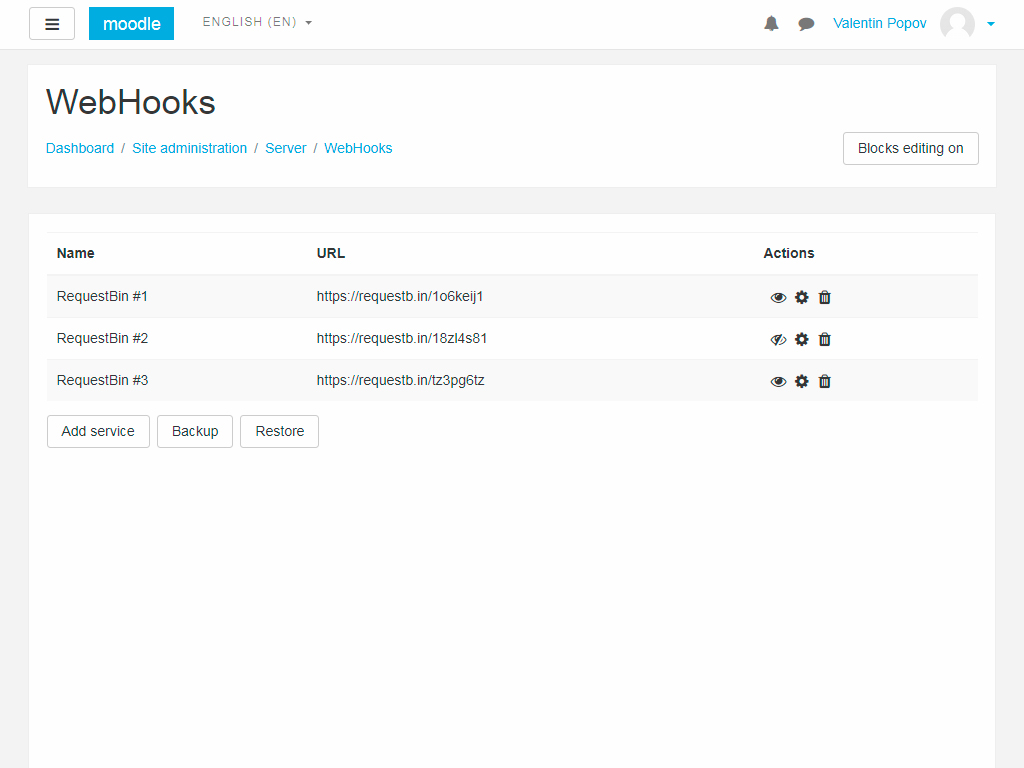
On the main page you can see the list of services and manage each service separately.
Column description
* "**Name**" shows the name of the service.
* "**URL**" indicates the address of the service to which notifications are received.
* "**Actions**" allows you to enable / disable the service, edit and delete.
Description of control buttons:
* "**Add service**" opens a page for creating a new service.
* "**Backup**" loads the backup file of the service list.
* "**Restore**" redirects the data recovery page from the backup.
### Guide to the editor
During the editing and creation of the service, this page opens:
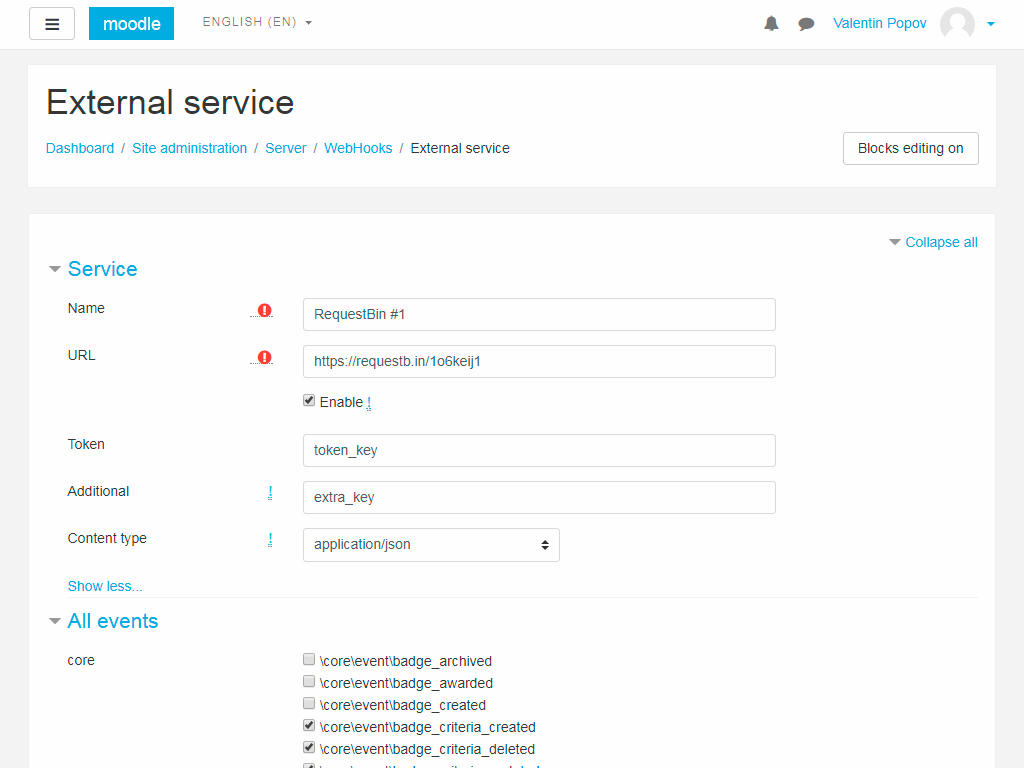
Description of fields:
* "**Name**" stores an arbitrary name for the service.
* "**URL**" stores the address of the service to which notifications will be sent as a POST request.
* "**Token**" allows you to specify an individual key that will allow an external service to identify requests.
* "**Advanced**" stores a large string passed to the service.
This can be useful for some services or users.
* "**Content Type**" allows you to configure the type of outbound requests if there are compatibility issues.
The "**All events**" list contains a list of all events registered in the system.
The selected events will notify the service.
## Request format
Events come in
[JSON](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JSON)
format.
An example of an observed course event:
```JSON
{
"eventname": "\\core\\event\\course_viewed",
"component": "core",
"action": "viewed",
"target": "course",
"objecttable": null,
"objectid": null,
"crud": "r",
"edulevel": 2,
"contextid": 2,
"contextlevel": 50,
"contextinstanceid": "1",
"userid": "2",
"courseid": "1",
"relateduserid": null,
"anonymous": 0,
"other": null,
"timecreated": 1512961456,
"host": "localhost",
"token": "",
"extra": ""
}
```
[Detailed description of the fields](https://docs.moodle.org/dev/Event_2#Properties).